MySQL to Redis Sync
Overview
This topic describes how to use BladePipe to move data from MySQL to Redis, including the following features:
- Support a single-node Redis instance, master/standby Redis instances, and a sharded cluster instance.
- Support setting a cache expiry time when writing data to a Redis instance.
Highlights
Automatical Adaptation to Redis Various Deployments
There are differences in the way of writing data between Redis sharded and non-sharded clusters.
BladePipe automatically identifies the deployment form of Redis by obtaining Redis parameters, and adjusts the writing method to run the Incremental DataJob normally.
Support for Cache Expiration
It is allowed to set the cache expiry time when writing data to a Redis instance.
When creating a BladePipe DataJob, you can optionally set the expiry time (seconds).
When a DataJob is running, BladePipe sets the expiry time automatically to achieve the business goal.
Procedure
Step 1: Install BladePipe
Before you begin, you need to prepare the tool. Download and install BladePipe.
Step 2: Add DataSources
In this example, a ApsaraDB for Redis and a self-managed MySQL instance are used.
- Log on to the BladePipe console.
- Click DataSource > Add DataSource, and add 2 DataSources.
If Redis is a cluster, you can fill in all nodes or all master nodes and separate them with commas.
Step 3: Create a DataJob
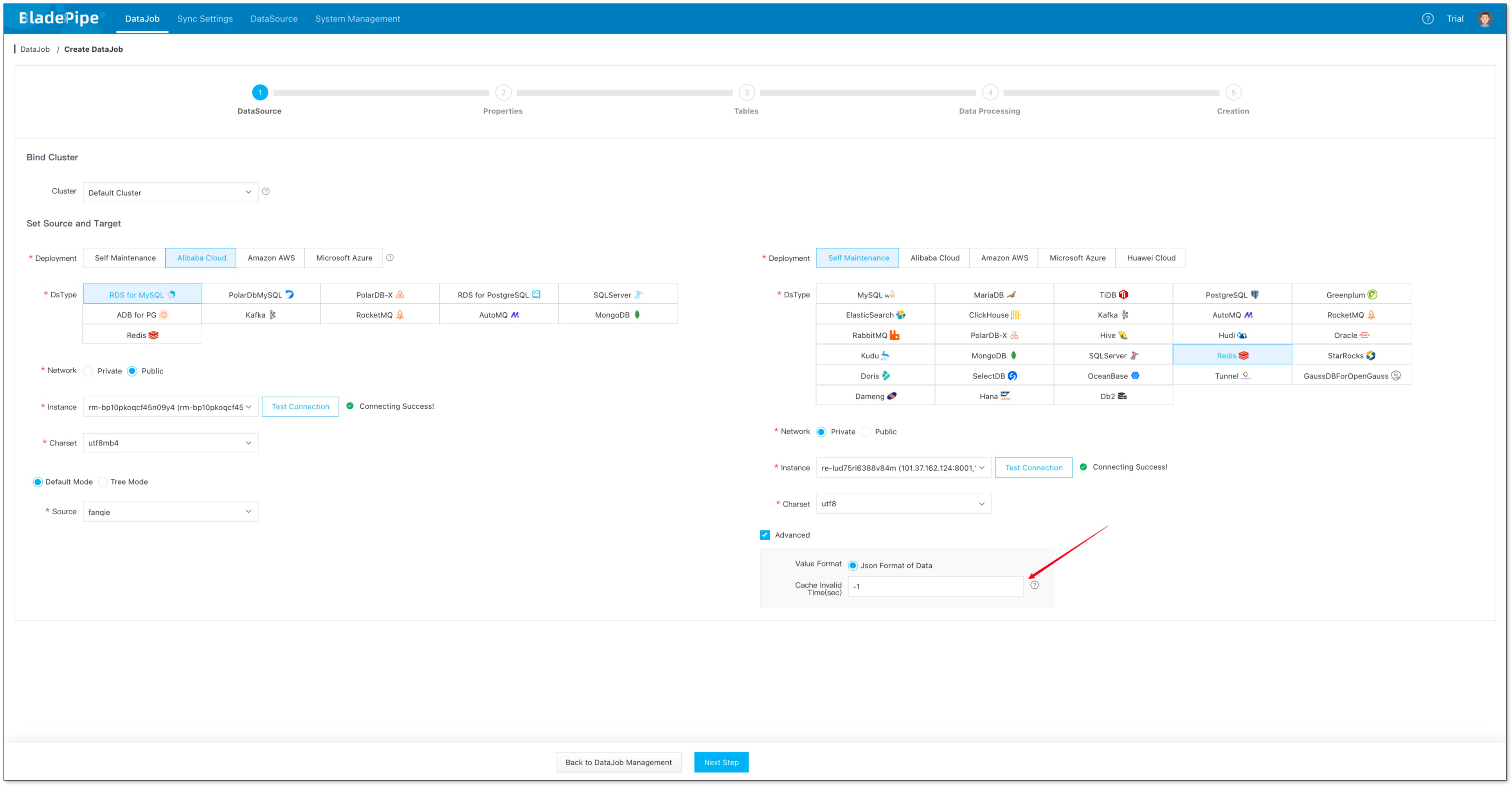
- Click DataJob > Create DataJob.
- Set the cache expiry time (second) in Advanced configuration of the target DataSource. The number <=0 means it is not set.
- Click Next Step.
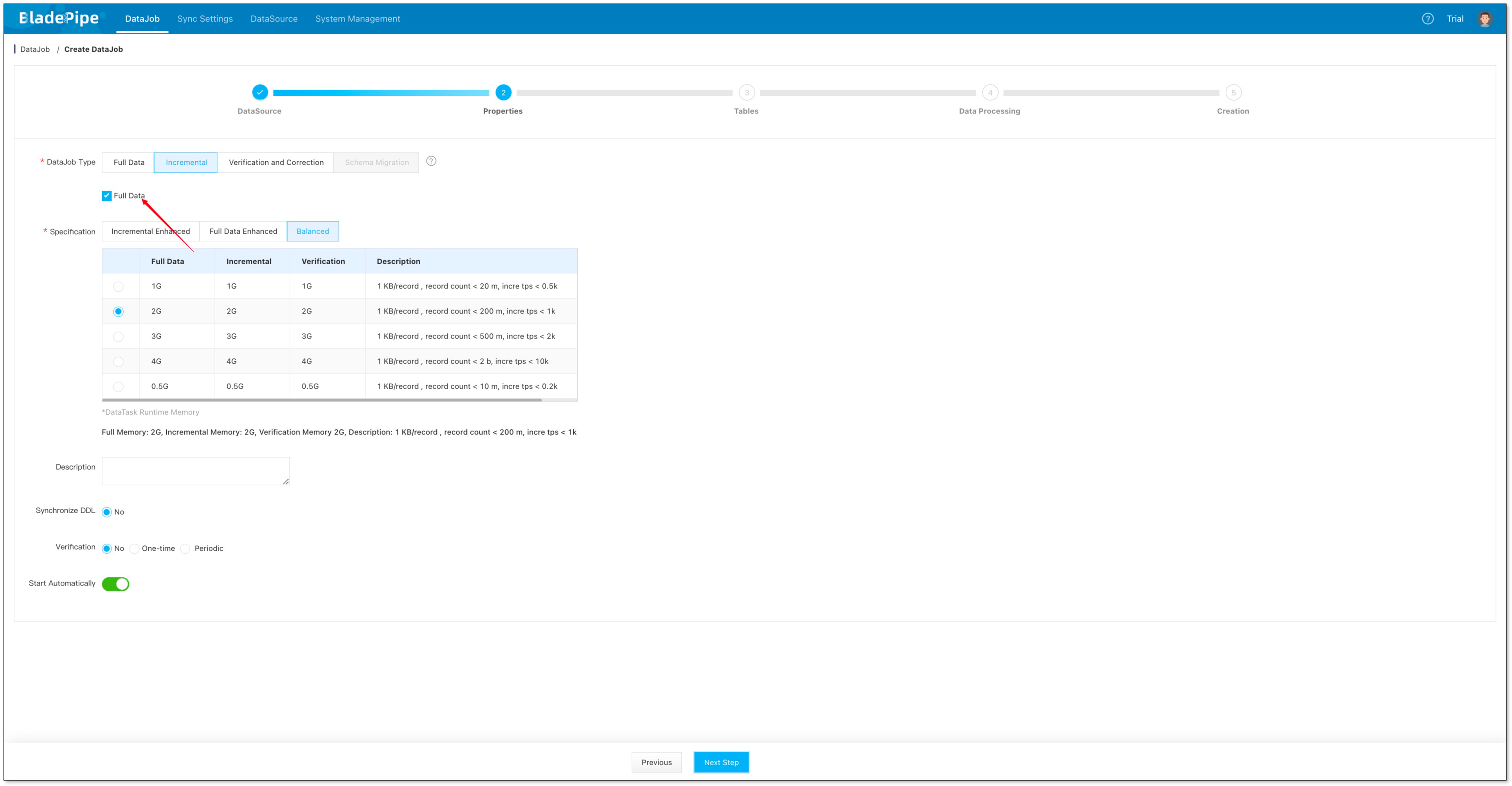
- Select Incremental, together with the Full Data option.
- Click Next Step.
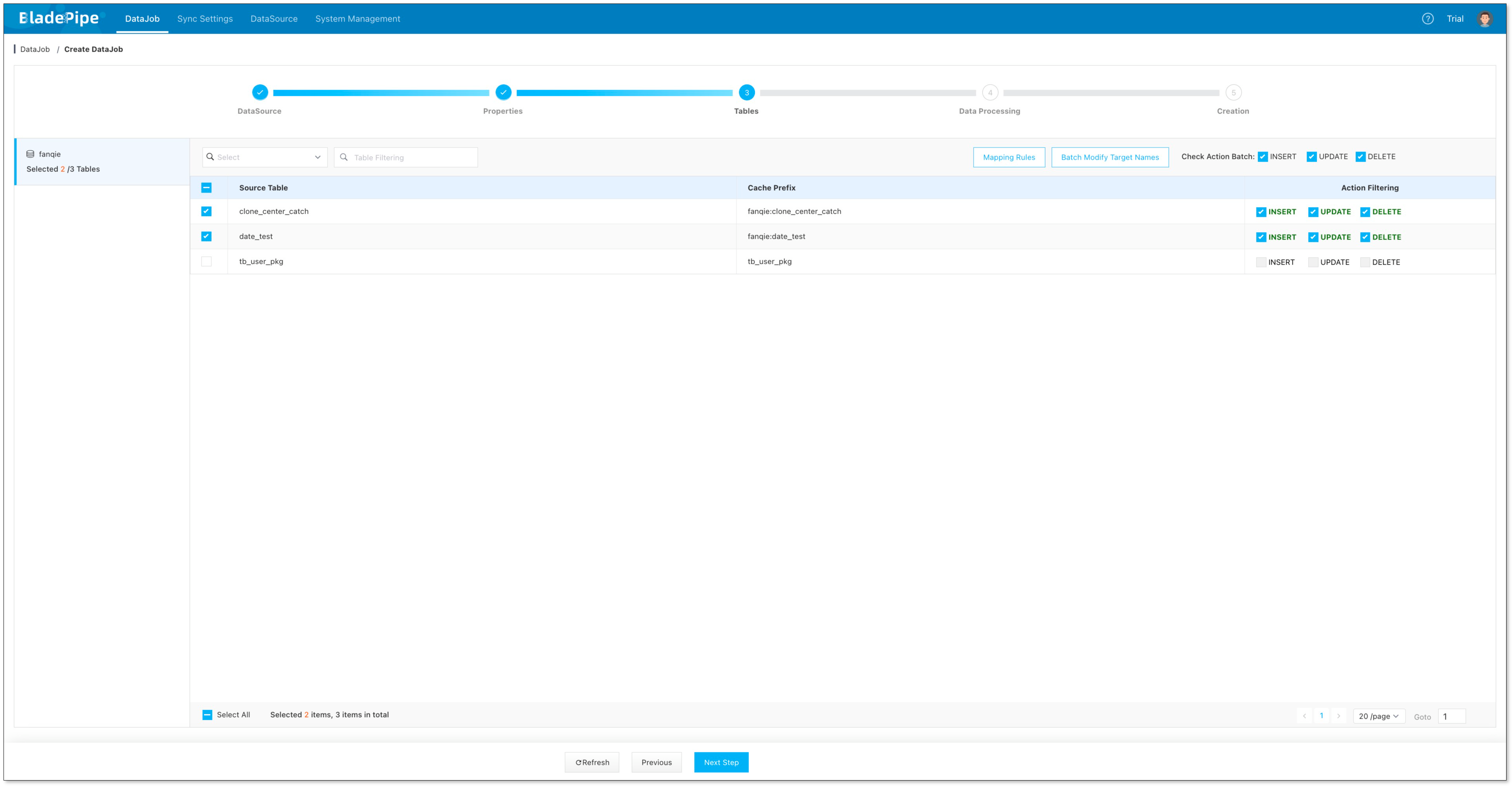
- Select the tables to be replicated and click Next Step.
Because the keys in Redis are composed of the primary keys of the source tables, it is not recommended to select the tables without a primary key.
- Select the columns to be replicated and click Next Step.
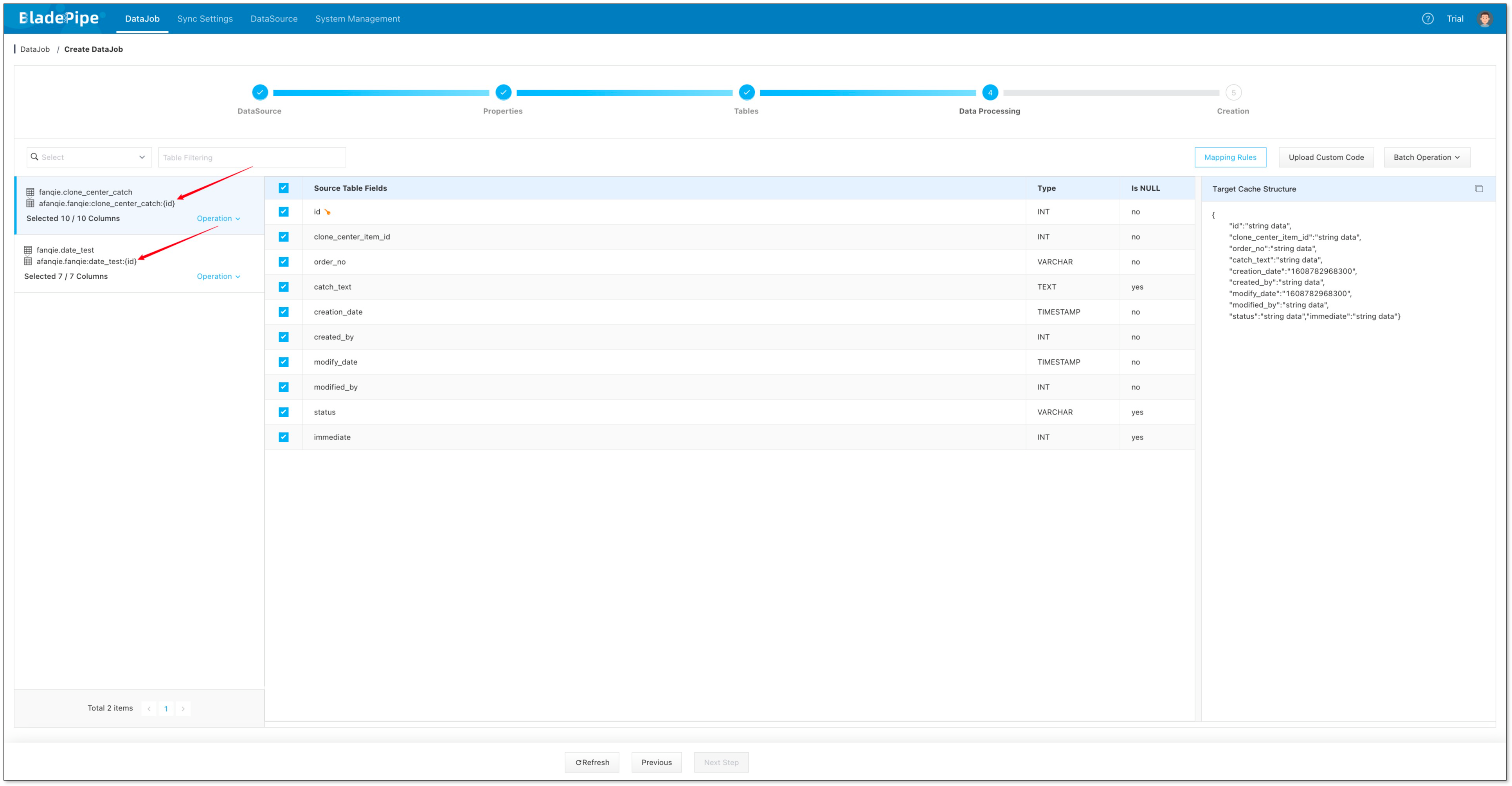
- Confirm the creation.
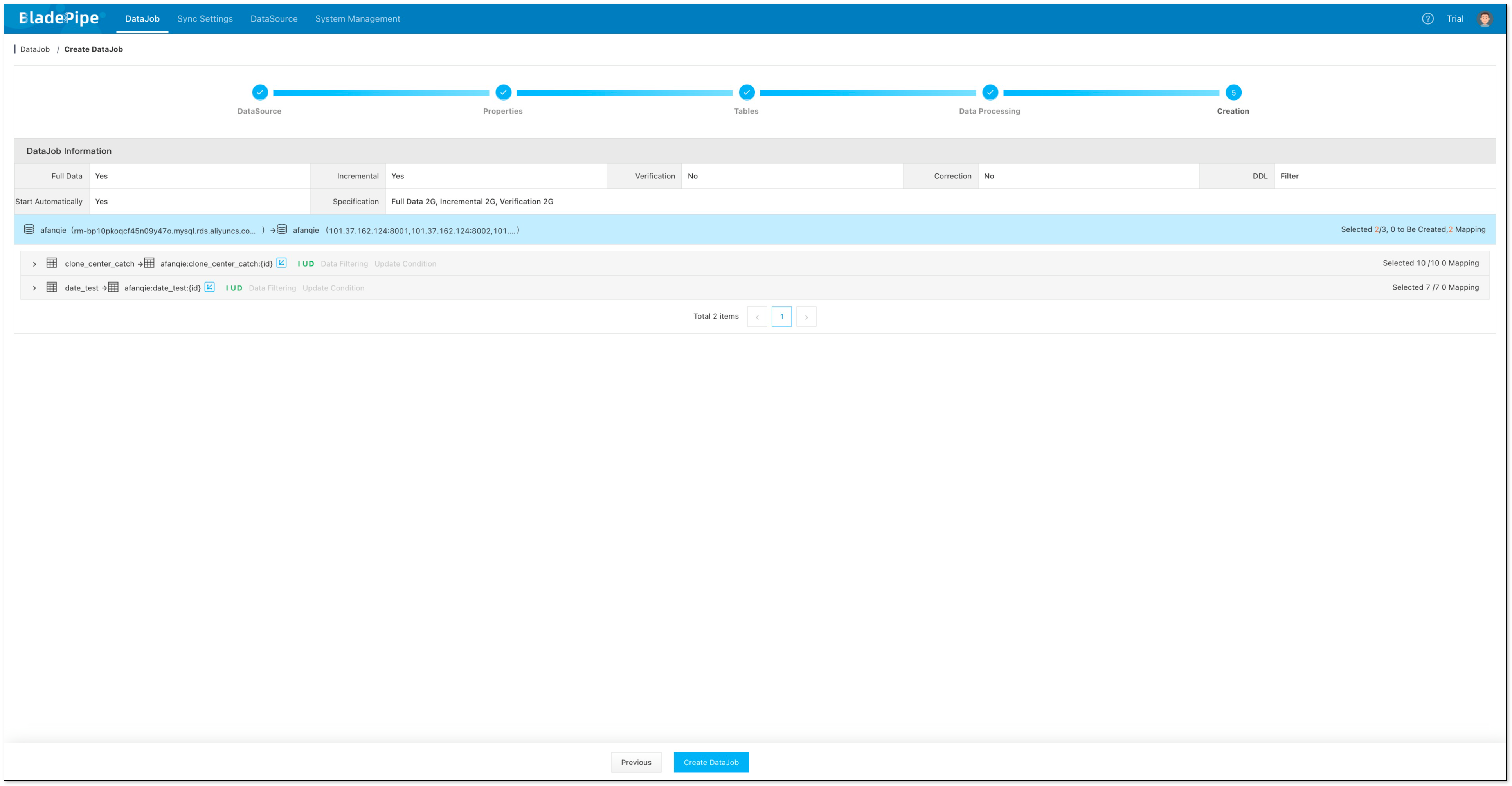
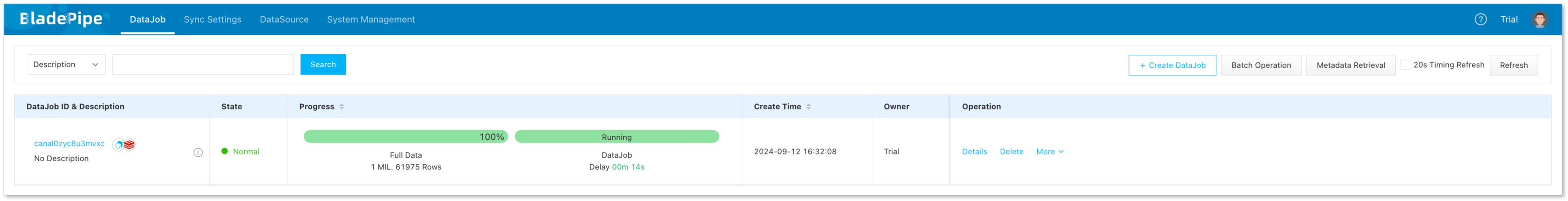
Test and Verify Data
- INSERT, UPDATE and DELETE data in the source instance.
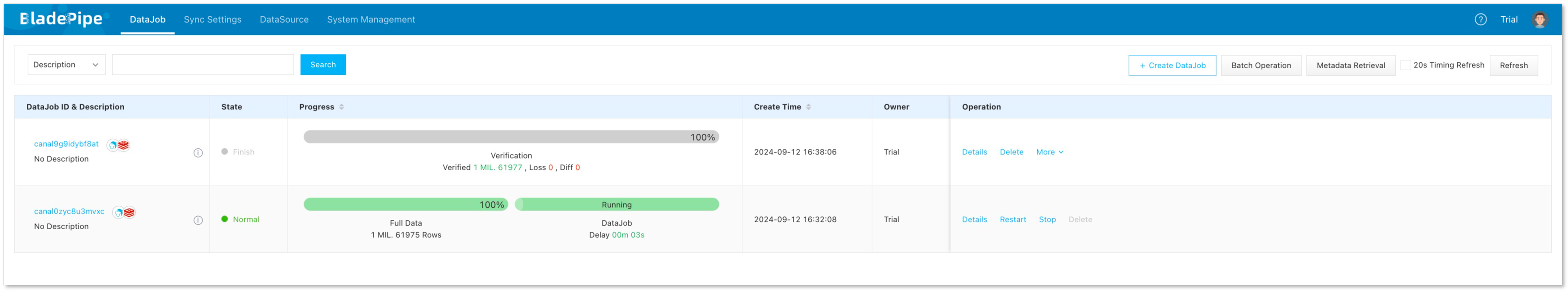
- Create a Data Verification DataJob, and the result shows that the data is consistent.
FAQ
What should I do after a Redis master/standby switchover?
BladePipe writes data with JedisCluster, which automatically senses a master/standby switchover.
What should I do if the nodes in Redis are changed?
You can manually modify the node information of the DataJob configuration and restart the DataJob.
Summary
This is a quick and easy guide to replicate data from MySQL to Redis with BladePipe, accelerating your business upgrade.