How to Move Data From MySQL to Redis in Real Time
Overview
Redis is an open-source, in-memory, non-relational data store known for its high performance and flexibility. It is widely used in a range of cases, such as real-time analysis, application cache, and session management. This makes it important to integrate data to Redis.
This tutorial delves into how to use BladePipe to move data from MySQL to Redis, including the following features:
- Support a single-node Redis instance, master/standby Redis instances, and a sharded cluster instance.
- Allow setting a cache expiration time when writing data to a Redis instance.
Highlights
Automatic Adaptation to Sharded Clusters
There are differences in the way of writing data to Redis sharded and non-sharded clusters.
BladePipe automatically identifies the cluster sharding of Redis by obtaining Redis parameters, and adjusts the data write method to run the Incremental DataJob.
Support for Cache Expiration
It is allowed to set the cache expiration time when writing data to a Redis instance.
When creating a BladePipe DataJob, you can optionally set the expiration time (in seconds). The configuration takes effects automatically when a DataJob is running.
Procedure
Step 1: Install BladePipe
Follow the instructions in Install Worker (Docker) or Install Worker (Binary) to download and install a BladePipe Worker.
Step 2: Add DataSources
-
Log in to the BladePipe Cloud.
-
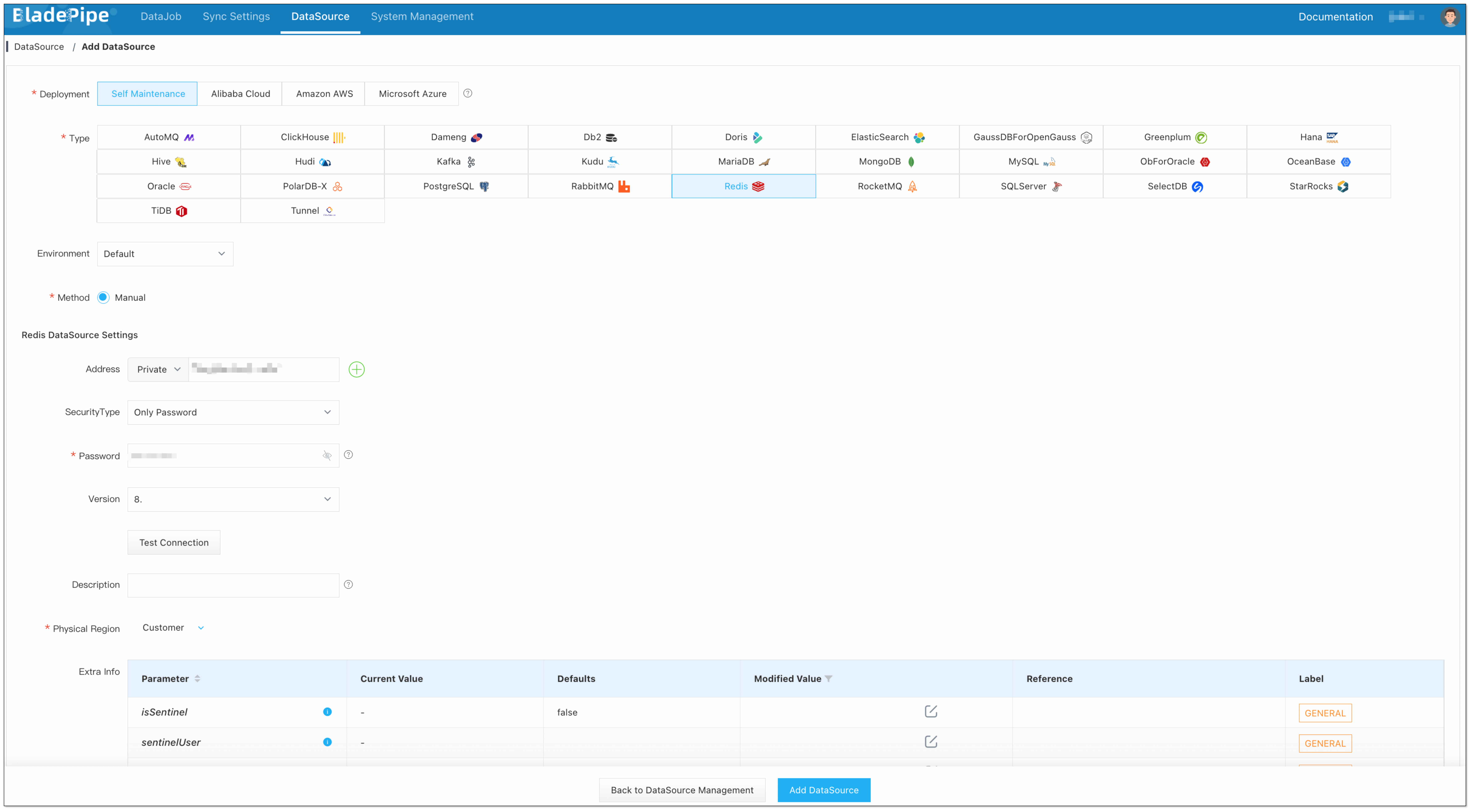
Click DataSource > Add DataSource.
-
Select the source and target DataSource type, and fill out the setup form respectively.
 信息
信息If the Redis instance is a cluster, please fill in all nodes or all master nodes and separate them with commas.
Step 3: Create a DataJob
-
Click DataJob > Create DataJob.
-
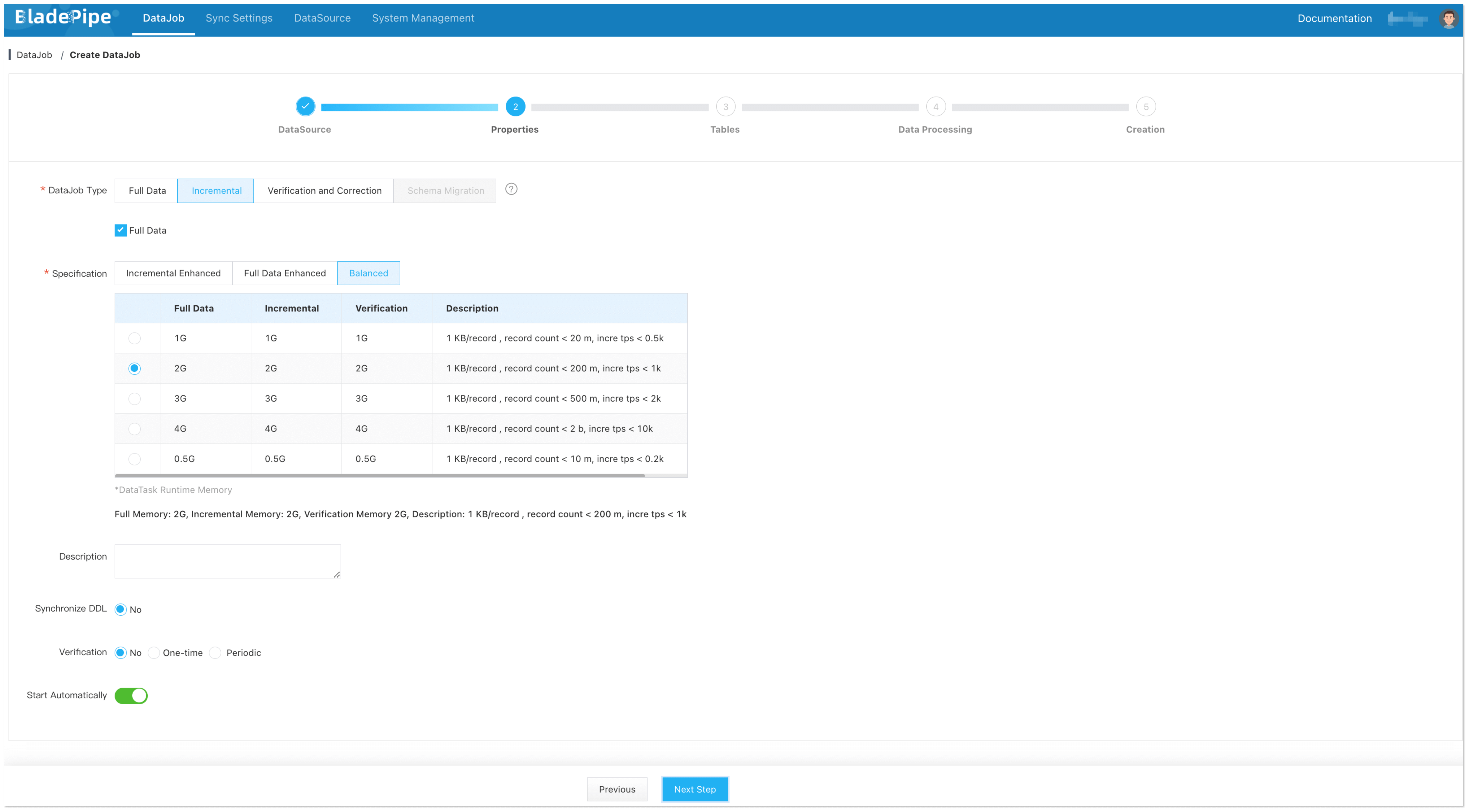
Select the source and target DataSources. Set the cache expiration time (in seconds) in Advanced configuration of the target DataSource. The number <=0 means the cache won't expire.

-
Select Incremental for DataJob Type, together with the Full Data option.
-
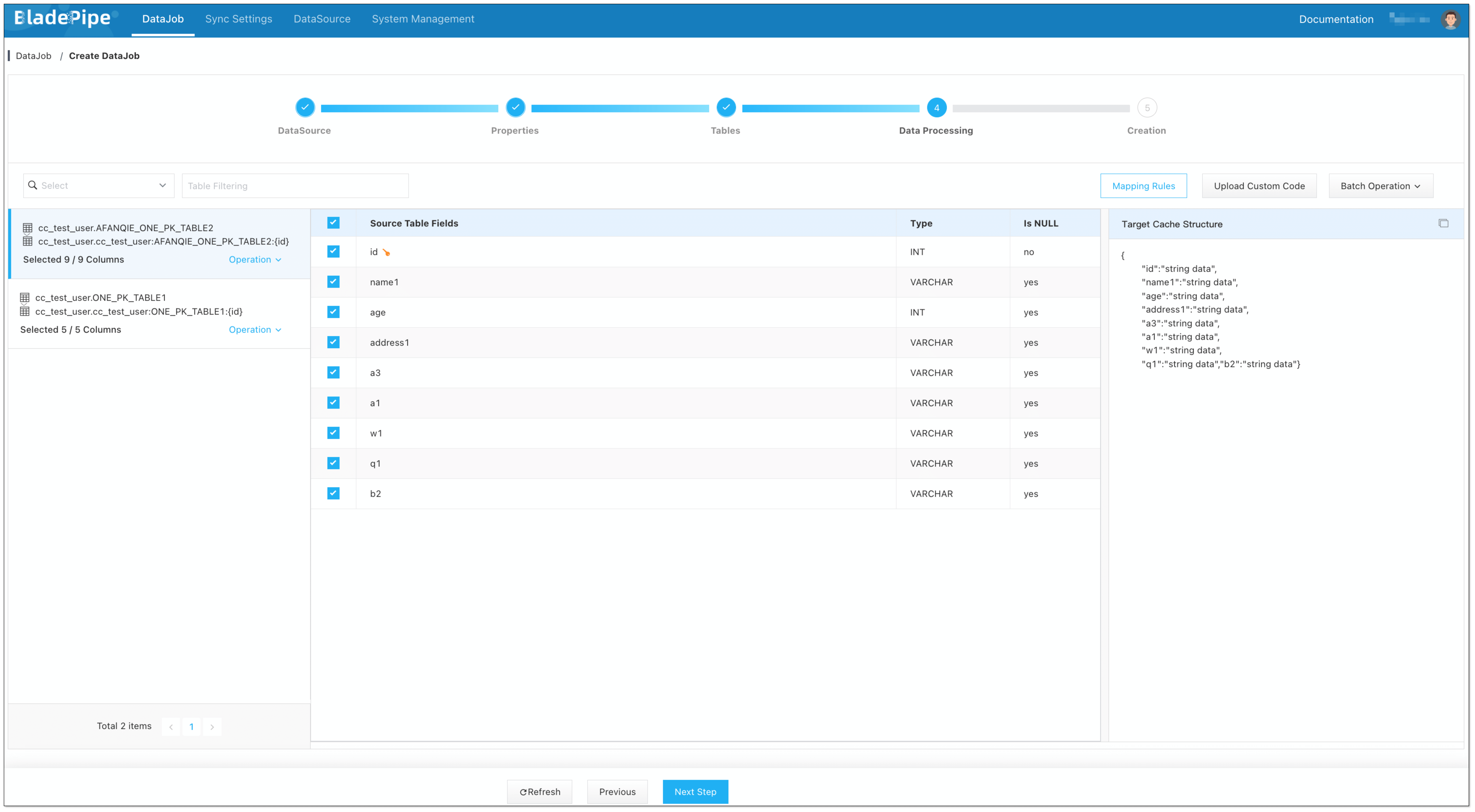
Select the tables to be replicated.
 信息
信息Because the keys in Redis are composed of the primary keys of the source tables, it is not recommended to select the tables without a primary key.
-
Select the columns to be replicated. Filter the data if needed.
-
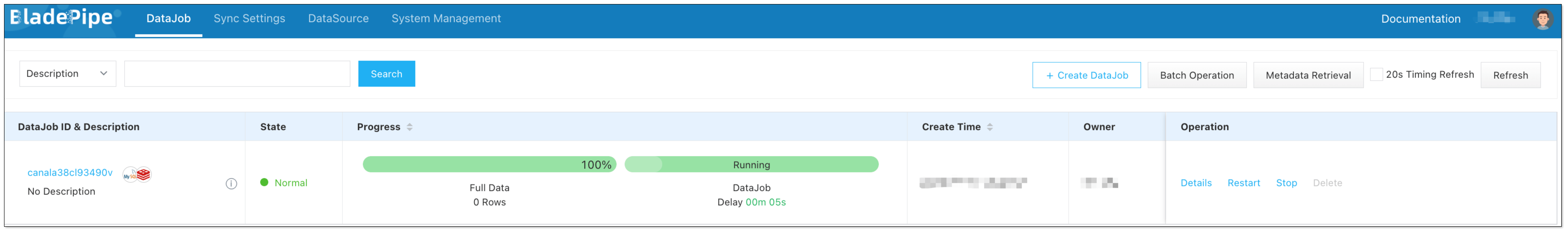
Confirm the creation.
信息The DataJob creation process involves several steps. Click Sync Settings > ConsoleJob, find the DataJob creation record, and click Details to view it.
The DataJob creation with a source MySQL instance includes the following steps:
- Schema Migration
- Allocation of DataJobs to BladePipe Workers
- Creation of DataJob FSM (Finite State Machine)
- Completion of DataJob Creation
-
Now the DataJob is created and started. BladePipe will automatically run the following DataTasks:
- Schema Migration: The schemas of the source tables will be migrated to the target instance.
- Full Data Migration: All existing data from the source tables will be fully migrated to the target instance.
- Incremental Data Synchronization: Ongoing data changes will be continuously synchronized to the target instance.
FAQ
What should I do after a Redis master/standby switchover?
BladePipe writes data with JedisCluster, which automatically senses a master/standby switchover.
What should I do if the nodes in Redis are changed?
You can manually modify the node information of the DataJob configuration and restart the DataJob.
